INDIBA radiofrequency works by enhancing the body’s metabolic pathways without disrupting normal cell physiology. The INDIBA treatment gradually and homogenously generates heat at selected areas of the body. The procedure triggers biological responses that lead to tissue regeneration which enables healing and body contouring to take place. We utilize INDIBA on our postoperative patients to assist in the healing process. This stimulates blood flow and lymphatic drainage from the treated areas, assisting in recovery and postoperative healing.
How is the treatment applied?
INDIBA combines two treatment modes. A capacitive mode that focuses on soft tissues, and a resistive mode for thick, fat and fibrotic tissues. When the treatment is applied to a specific area, it enables the correct movement of ions through the cell membrane. This works through its unique radiofrequency and a gradual increase in the skin’s temperature. It is painless and safe to the skin’s external layer. Electrodes are applied to the skin and a soft massaging action is used. During treatment heat is safely generated and patients experience a pleasant warming sensation.
What to Expect
INDIBA uses radio frequency energy in two modes – Capacitive and Resistive Mode. The Capacitive Electrode (CET) stimulates energy points, a unique and important step to promote lymphatic drainage; and the Resistive Electrode (RET) is able to penetrate and increase the internal temperature which acts effectively on more fibrotic tissues.
Downtime
With INDIBA, there will be no downtime. After your treatment, you can resume your normal activities immediately.
Recovery
The skin might appear flushed at first, but the redness should disappear within a few hours. Some people experience slight swelling, tingling or tenderness to the touch, but these are temporary.
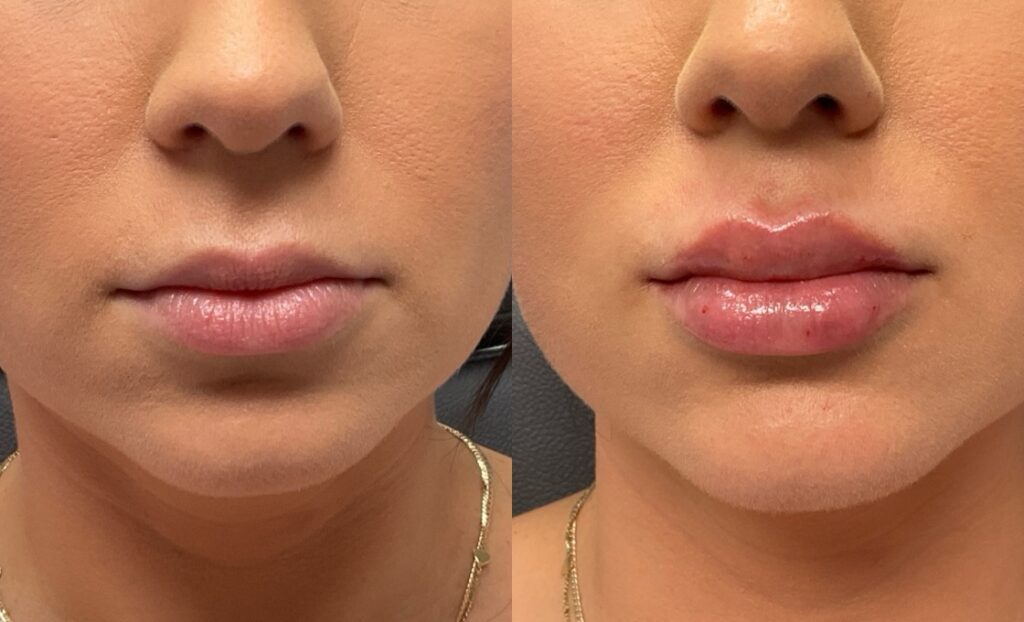
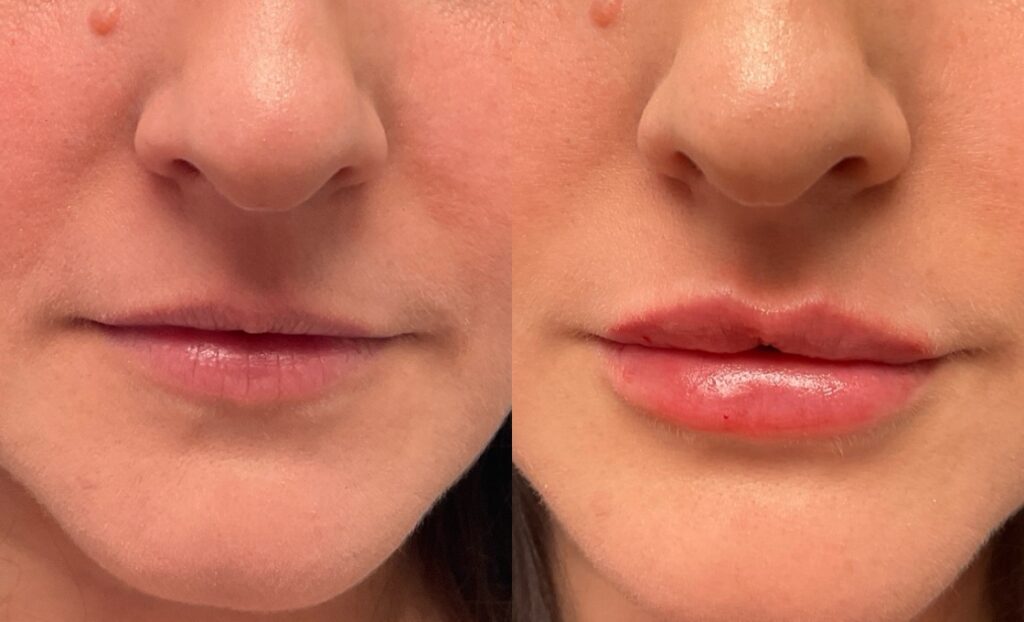
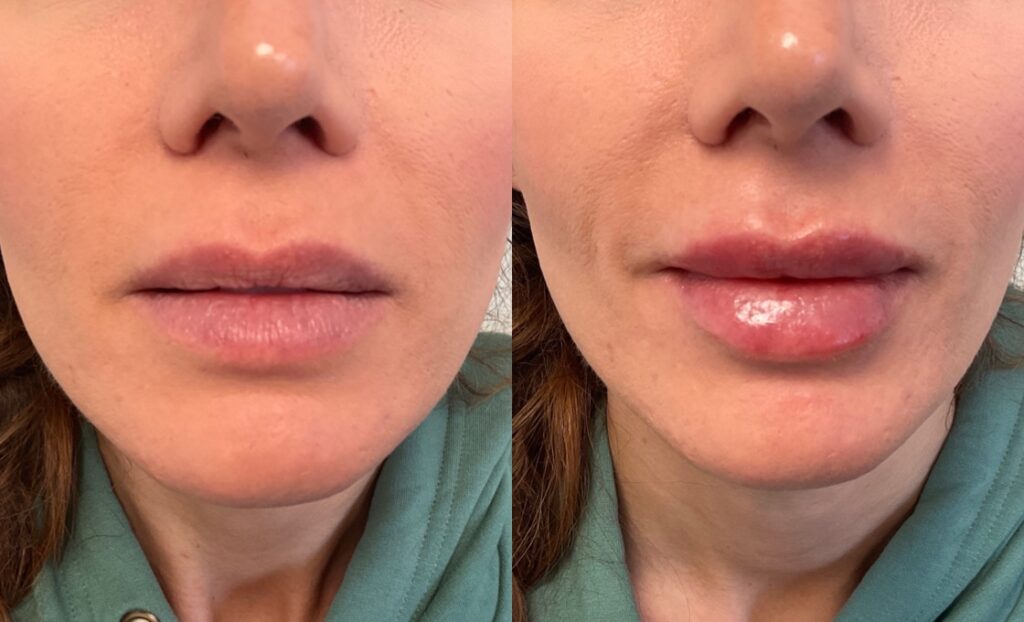
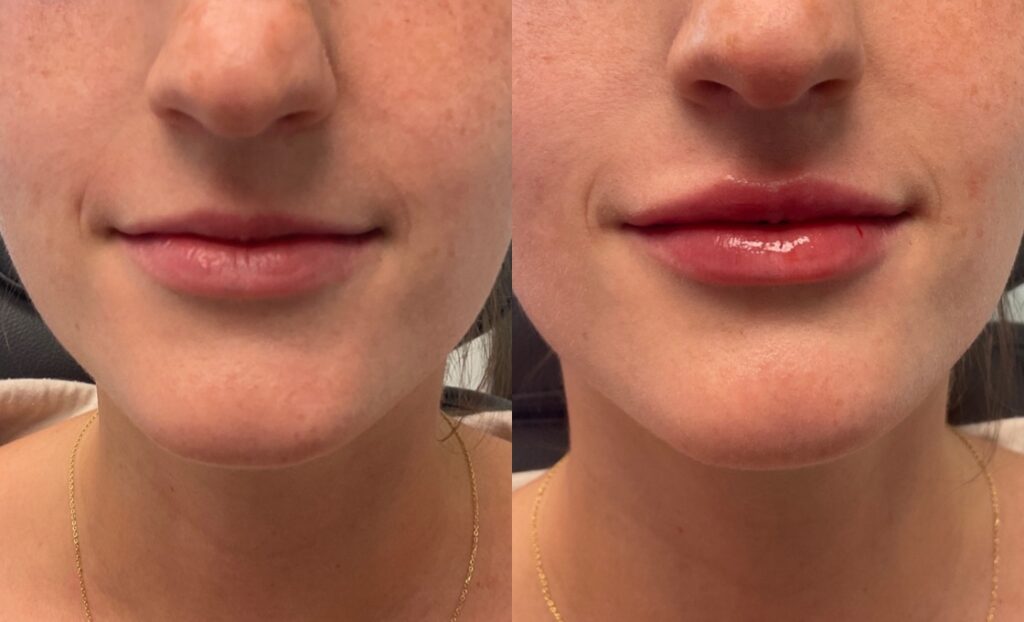
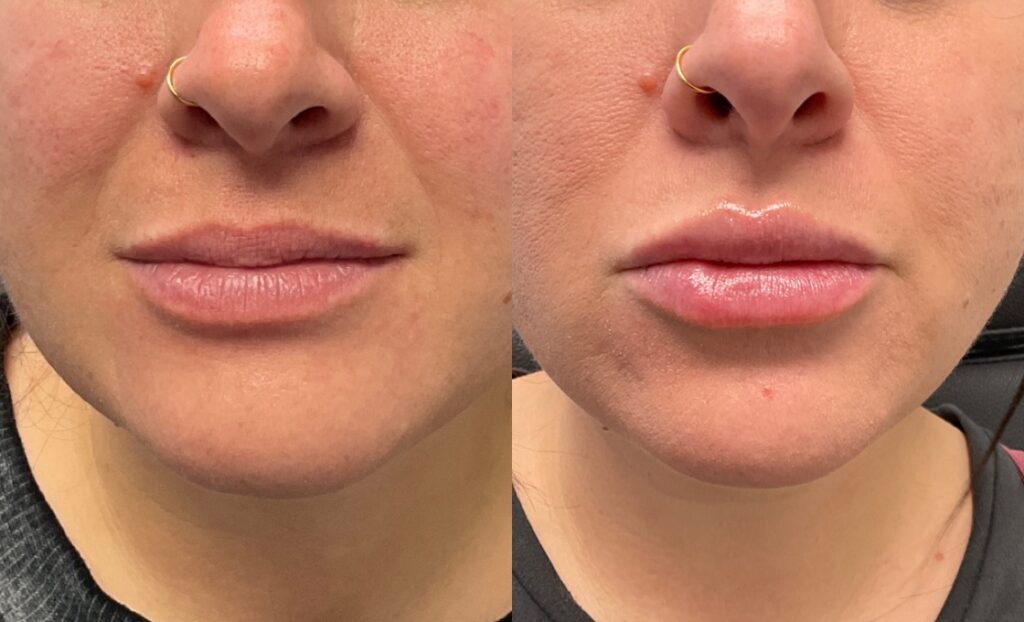
Non-Surgical Before & After Gallery
Discover Your Confidence & Unveil Your True Beauty
Contact Lincoln, Nebraska’s premier cosmetic surgery practice, where your journey to enhanced beauty and newfound confidence begins.